CS140 -- Final Exam. December 10, 2008
Please, write your answers on a separate sheet, not on the exam.
Remember your name, too...
Question 1
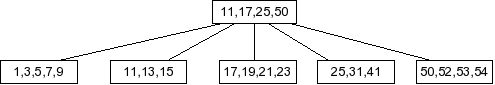
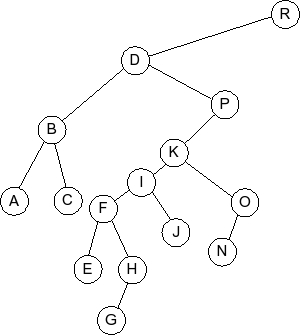
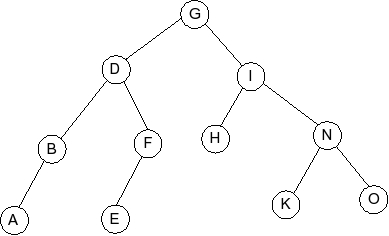
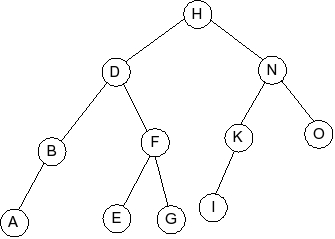
Behold the following B-tree for M = 5.
- Part 1: Draw the B-tree that results when you insert the value 6 into the tree.
- Part 2: Explain why a B-tree would have different values of M for internal
and external nodes of the tree.
Question 2
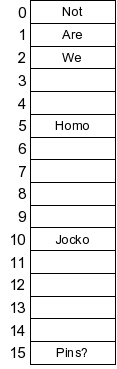
You are given the hash table on the right.
- Part 1: Suppose you are using
Linear Probing. Draw the hash table that results
when you insert the keys "Teachers" and "Critics", which
have hash values of 47 and 170 respectively.
- Part 2: Use the hash table on the
right to demonstrate why quadratic probing can
be a disastrous collision resolution technique
if you don't select your parameters properly.
Use a detailed example, and then tell me how you
would change things to make quadratic probing
work.
- Extra Credit: Who wrote the song?
|
|
Question 3
Let f(x) = 2x, g(x) = 100x, h(x) = |x - 3|, and j(x) = -|x - 3|.
Which of
the following are true (answer all that are true, not just one):
| A: f(x) = O(g(x)) |
| D: g(x) = O(f(x)) |
| G: h(x) = O(f(x)) |
| J: j(x) = O(f(x)) |
| B: f(x) = O(h(x)) |
| E: g(x) = O(h(x)) |
| H: h(x) = O(g(x)) |
| K: j(x) = O(g(x)) |
| C: f(x) = O(j(x)) |
| F: g(x) = O(j(x)) |
| I: h(x) = O(j(x)) |
| L: j(x) = O(h(x)) |
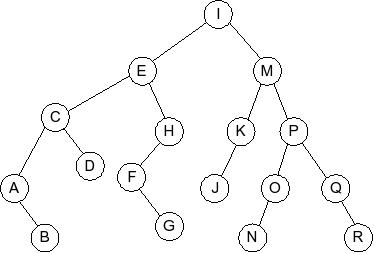
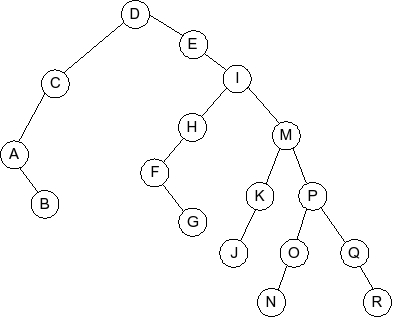
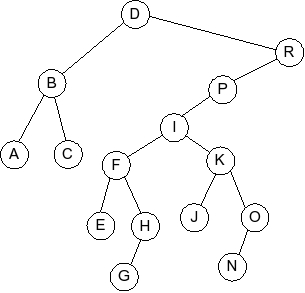
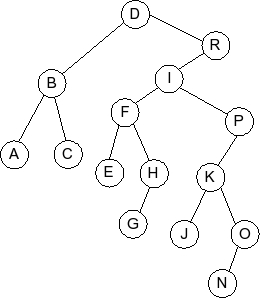
Question 4
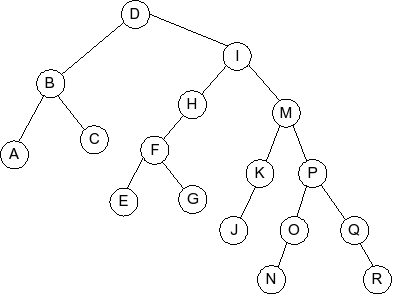
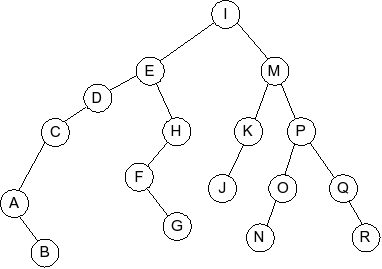
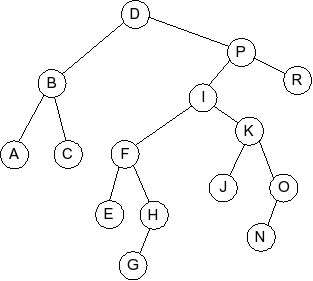
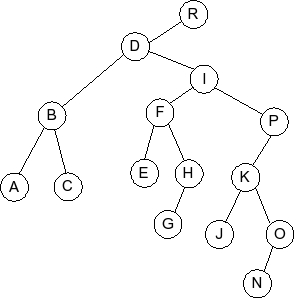
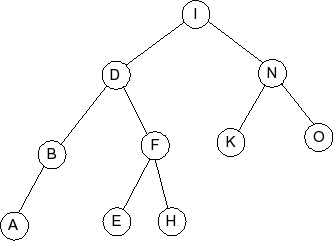
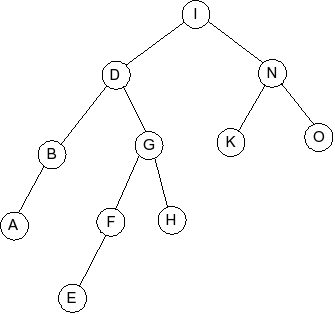
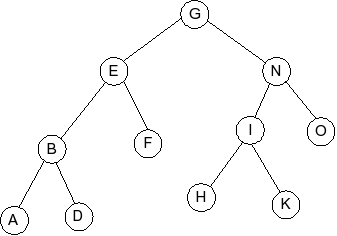
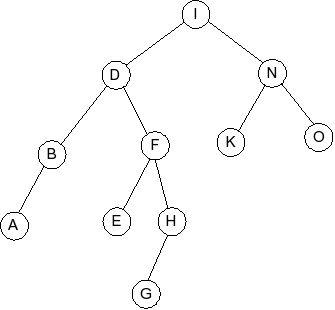
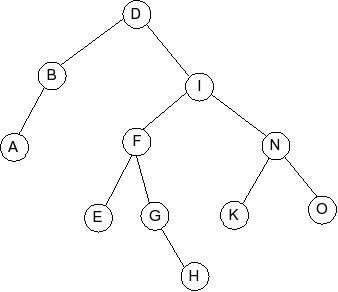
Given the following splay tree:
Which of the following is the tree that results when D is inserted into
the splay tree:
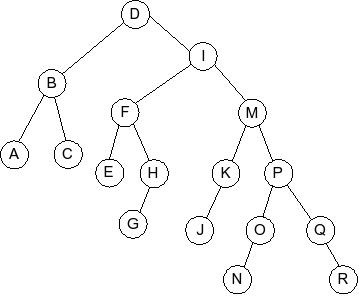
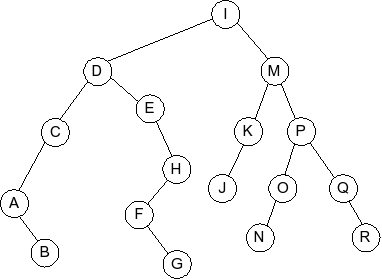
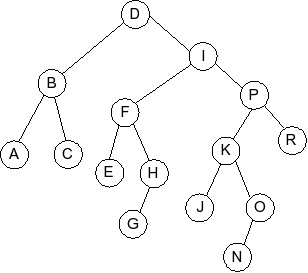
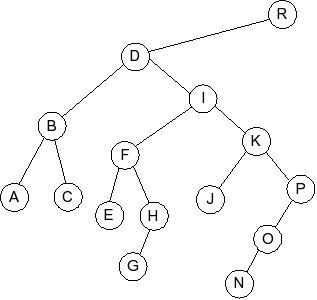
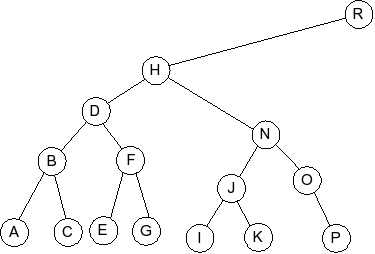
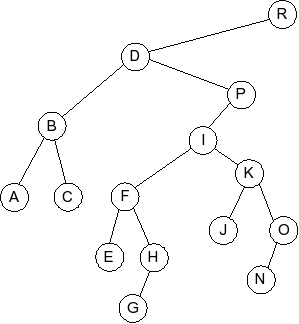
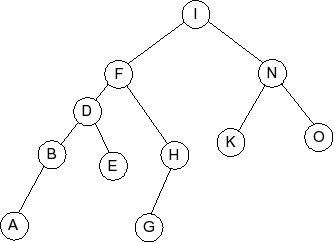
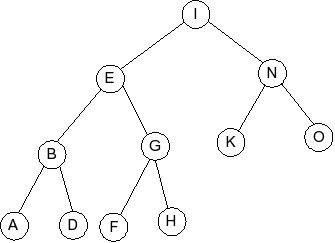
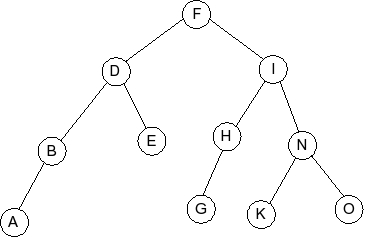
Question 5
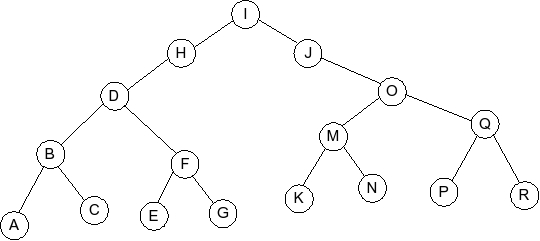
Given the following splay tree:
Which of the following is the tree that results when R is inserted into
the splay tree:
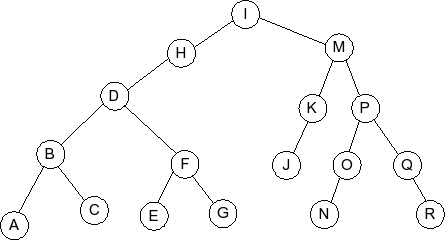
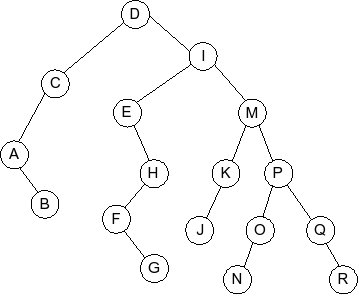
Question 6
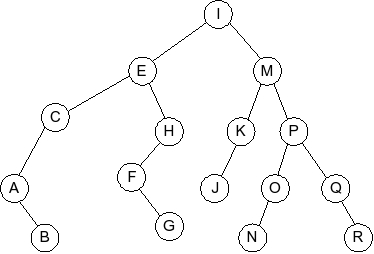
Given the following AVL tree:
Which of the following is the tree that results when G is inserted into
the AVL tree:
Question 7
Recall the header file for Disjoint Sets, below left.
typedef struct {
int *links;
int *sizes;
int *ranks;
int maxindex;
int nsets;
} DisjointSet;
extern DisjointSet *new_disjoint_set(int maxindex);
extern void free_disjoint_set(DisjointSet *dj);
extern void disjoint_makeset(DisjointSet *dj, int index);
extern int disjoint_union(DisjointSet *dj, int s1, int s2);
extern int disjoint_find(DisjointSet *dj, int index);
|  |
Suppose we have a DisjointSet struct whose state is depicted above right,
and we have a pointer to it in the variable dj.
Answer the following questions:
- Part A: is disjoint_find(dj, 0) equal to disjoint_find(dj, 1)?
- Part B: is disjoint_find(dj, 0) equal to disjoint_find(dj, 2)?
- Part C: is disjoint_find(dj, 2) equal to disjoint_find(dj, 4)?
- Part D: Draw the state of the struct when
disjoint_union(dj, 4, 7) is called. Draw everything (links, sizes, ranks, maxindex
and nsets). Assume "union by ranks" is used.
Question 8
Write a program that takes two command line arguments, a and b,
and prints out all strings that have a A's and b B's.
Question 9
Suppose we have the following typedef for a tree node:
typedef struct node {
char *key;
int nchildren;
struct node **children;
} Node;
|
The variable nchildren is the number of children that a node has, and
children is an array of pointers to the children. Write a procedure
tree_size(Node *n), which returns the number of nodes in the tree
rooted at node n.