CS202 Midterm - March 9, 2023 - Answers and Grading
James S. Plank
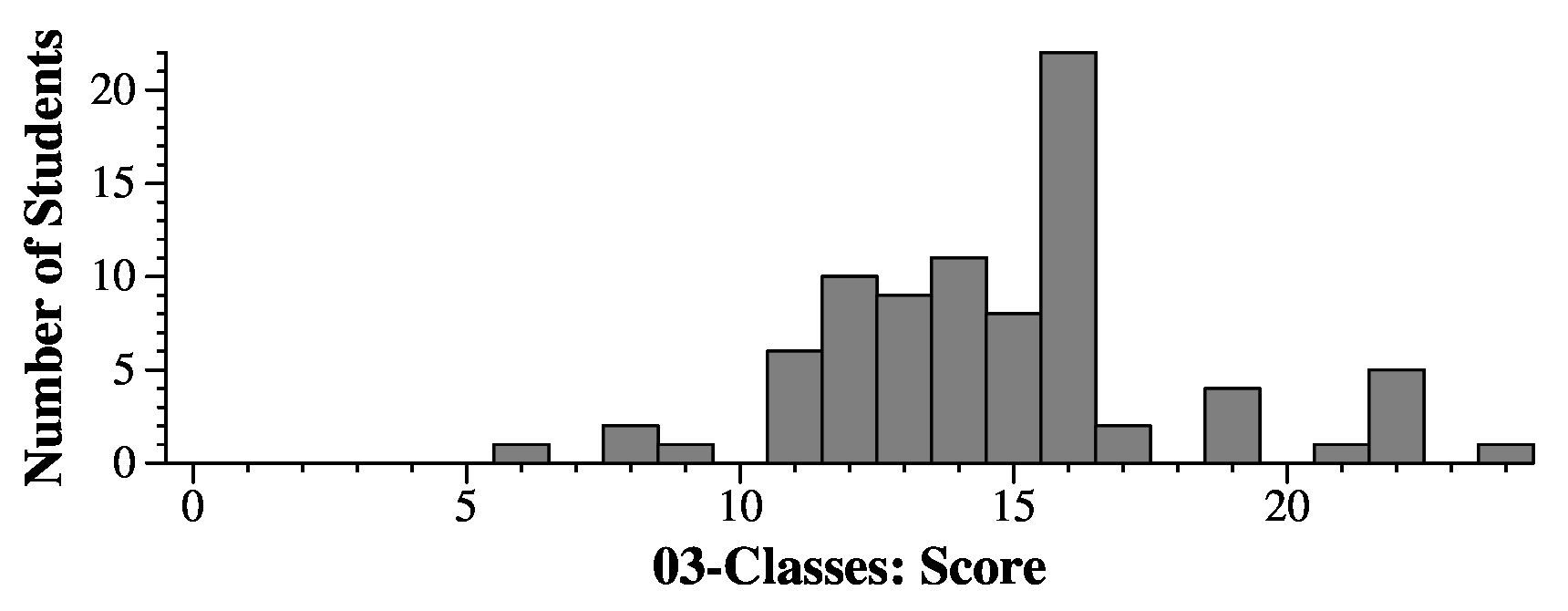
Question 3
- A. Animal is a class that exhibits polymorphism: True.
The method ggg() has two implementations that differ
based on the types of their arguments.
- B. Animal defines a customized copy constructor: True.
That is the following line in Animal.cpp:
- C. Animal defines a customized assignment overload: False.
Please see the lecture notes for how you define that.
- D. Please tell me the value of s1 just before main()
returns. s1 is set to "simba", and then it is the first parameter
to ggg(). That is not a reference parameter, so it is copied,
and s1 is unchanged. The answer is "simba".
- E. Please tell me the value of s2 just before main()
returns. s2 is set to "jaba", and then it is the first parameter
to hhh(). That is not a reference parameter, so it is copied,
and s2 is unchanged. The answer is "jaba".
- F. Please tell me the value of t1 just before main()
returns. t1 is set to "tony", and then it is the second parameter
to ggg(). That is a reference parameter, so ggg() could
change it. It could be anything. The answer is "multiple".
- G. Please tell me the value of t2 just before main()
returns. t2 is set to "speedy", and then it is the second parameter
to hhh(). That is a const reference parameter, so
and t2 is unchanged. The answer is "speedy".
- H. Please tell me the value of i1 just before main()
returns. i1 is set to 75, and then it is the parameter
to ggg(). It is a reference parameter, so its value could
by anything afterwards. The answer is "multiple".
- I. Please tell me the value of i2 just before main()
returns. i2 is set to 85, and then it is the parameter
to iii(). It is a const reference parameter, so its value cannot
be changed. The answer is 85.
- J. Please tell me the value of a1.tiger just before main()
returns. a1.tiger is set to "sherekhan", and then
a1.ggg() is called. Since ggg() is const, a1.tiger won't be
changed. The answer is "sherekhan".
- K. Please tell me the value of a2.tiger just before main()
returns. a2 is copied from a1, and then
a2.ggg() is called. Since ggg() is const, a2.tiger won't be
changed. The answer is "sherekhan".
- L. Please tell me the value of a3.tiger just before main()
returns. a3.tiger is set to "speedy", and then
a3.hhh() is called. Since hhh() is not const, a3.tiger can
be anything afterwards. The answer is "multiple".
- M. Please tell me the value of a4.tiger just before main()
returns. a4.tiger is set to "hangry", and then
a4.iii() is called. Since iii() is not const, a4.tiger can
be anything afterwards. The answer is "multiple".
- N. Please tell me the value of av.at(0).tiger just before main()
returns. av.at(0).tiger is set to "lazy", and then
av is resized. However, that resizing can't change av.at(0), so
The answer is "lazy".
- O. Please tell me the value of av.at(1).tiger just before main()
returns. When av is resized to 4, av[1] will be initialized by the
copy constructor. Since we don't know how that is implemented,
av.at(1).tiger can be anything.
The answer is "multiple".
Here's a table of the correct answers:
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
|
Fred
True.
True.
False.
spot
elsie
multiple
jenner
multiple
85
rex
rex
multiple
multiple
moomoo
multiple
|
Barn
True.
True.
False.
sweater
fran
multiple
bruce
multiple
85
baba
baba
multiple
multiple
wooly
multiple
|
Animal
True.
True.
False.
simba
jaba
multiple
speedy
multiple
85
sherekhan
sherekhan
multiple
multiple
lazy
multiple
|
Hoof
True.
True.
False.
flo
venison
multiple
hartford
multiple
85
bambi
bambi
multiple
multiple
bleh
multiple
|
Bug
True.
True.
False.
dots
blinky
multiple
buzz
multiple
85
watt
watt
multiple
multiple
henry
multiple
|
Grading
Parts A throuugh C were two points each. The rest were 1.5 points.
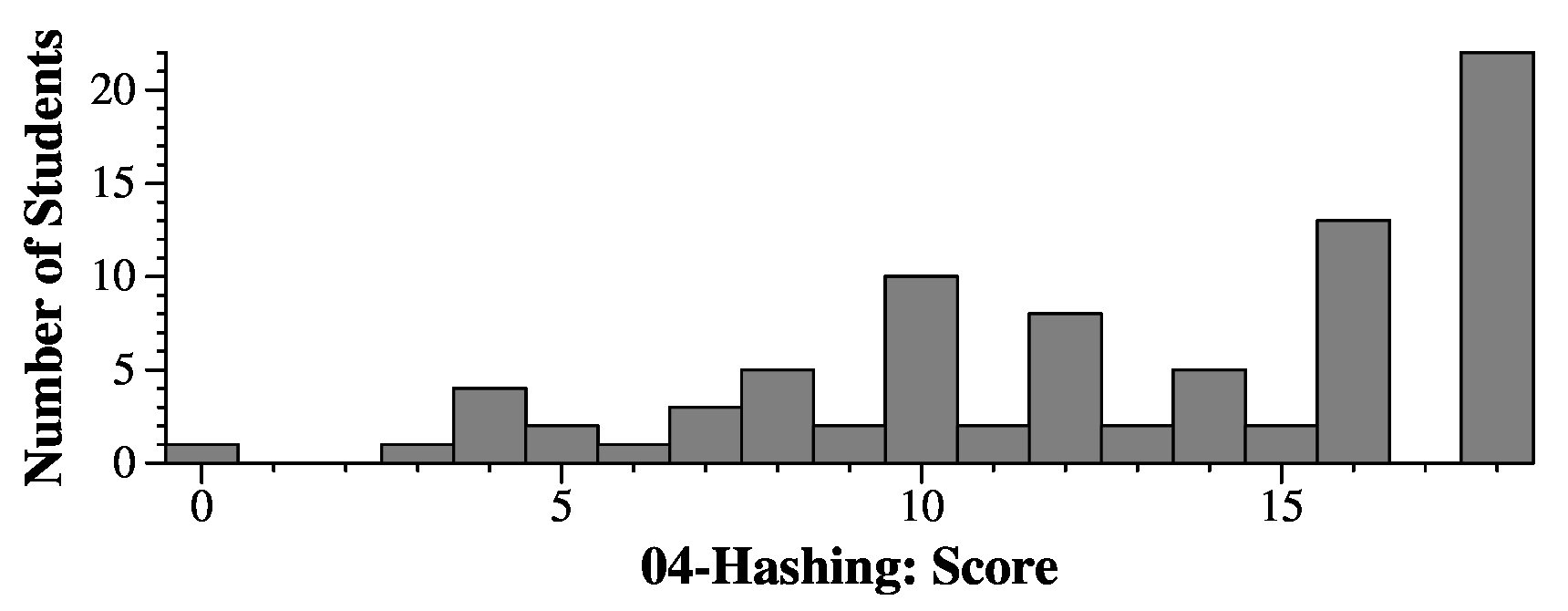
Question 4
- A: 369033 hashes to 13. Indices 13, 14, 15, 16 are taken, so the answer is 17.
- B: 1077784 hashes to 4 and the second hash will increment the value
by 5. Indices 4, 9, 14 and 19 are taken, so there is no answer: -1.
- C: 62794 hashes to 14 and the second hash will increment the value by
19. Indices 13 and 12 are taken, so the answer is 11.
- D: 1320609 hashes to 9. Index 9 is taken, so the answer is 10.
- E: 342232 hashes to 12. Indices 12, 13 and 16 are taken, so the answer
is (12+9) mod 20 = 1.
- F: 418294 hashes to 14. Indices 14, 15 are taken, so the answer is
is (14+4) mod 20 = 18.
- G: 1573160 hashes to 0. The answer is 0
- H: 413252 hashes to 12 and the second hash will increment the value by
8. Index 12 is taken, so the answer is (12+8) mod 20 = 0.
- I: 1108415 hashes to 15. Indices 15, 16, 19 and 4 are taken, so the answer
is (15+16) mod 20 = 11.
Here are all of the answers sorted by the value being hashed:
21216 0
62794 11
117156 0
148026 -1
342232 1
369033 17
396148 12
413252 0
418294 18
442954 3
446936 -1
565904 13
607907 3
611833 13
683442 18
694279 1
711201 2
824760 0
874614 18
875579 0
903535 4
920434 5
939140 4
945008 8
950336 3
1077784 -1
1090745 9
1104489 -1
1108415 11
1227626 8
1242237 1
1316015 11
1320609 10
1335465 1
1410088 12
1521186 7
1557280 4
1573160 0
1584886 7
1591584 8
1623214 0
1642628 8
1670764 10
1822849 -1
1903030 19
Grading
Each question was worth 2 points. If your starting index was off by ten, but you
got the problem correct with that starting index, you got 0.8 points.
Questions 5 through 10
You can compile and run these yourself. Here are the example answers:
5: qncaode
6: 25
7: 2915
8: 3821945067
9: 691732994025
10: fcebd
And here are all of the answers with the cpp filename as a key.
Question 5
aft: qncaode
dark: hrsfiez
liz: mdgnslf
pond: trpimhz
wive: tlganev
|
Question 6
lit: 23
nigh: 22
soon: 24
teal: 25
weep: 24
|
Question 7
mung: 2567
page: 2412
puny: 2691
sal: 2859
shin: 2915
|
Question 8
fowl: 0561243789
joey: 1795468320
sat: 3821945067
viz: 5130296748
zeus: 5084317629
|
Question 9
aile: 544529389468
bare: 62551787734
bee: 471726706031
jeep: 691732994025
push: 369023481054
|
Question 10
deck: fcebd
gyp: fcebd
prey: fcebd
shaw: fcebd
soar: fcebd
|
Grading
Two points each for questions 5 through 7. Three for questions 8 through 10.
On question 8, I gave:
- Q8: 0.5 points for the right starting letter and < 4 chars.
- Q8: 1 point for the right starting letter and >= 4 chars.
- Q8: 1 point for having exactly 10 characters.
- Q9: 1 point for the correct starting number
- Q10: Gave partial credit to answers like "a5a2a4a1a3". push_back() is pushing
back a character and not a string.
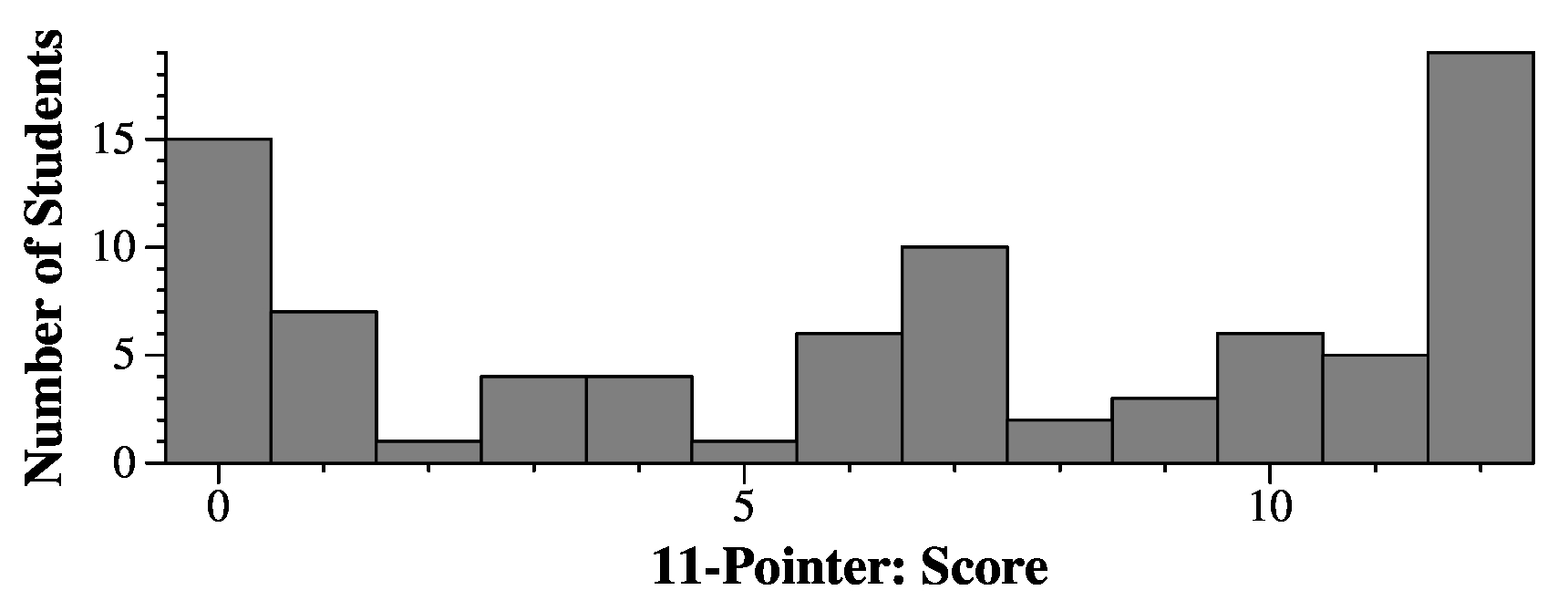
Question 11
We first read in *(p[i]):
- *(p[0]) = 44
- *(p[1]) = 69
- *(p[2]) = 24
- *(p[3]) = 88
We then read in four values of n and use them to set q and a:
- q[0] points to p[2], whose value is 24. So a[0] becomes 24.
- q[1] points to p[0], whose value is 44. So a[1] becomes 44.
- q[2] points to p[0], whose value is 44. So a[2] becomes 44.
- q[3] points to p[1], whose value is 69. So a[3] becomes 69.
We then read in four values of n and use them to increment *(p[i]):
- *(p[0]) is incremented by 1, becoming 45. That means *q[1] and *q[2] become 45.
- *(p[1]) is incremented by 8, becoming 77. That means *q[3] becomes 77.
- *(p[2]) is incremented by 3, becoming 27. That means *q[0] becomes 27.
- *(p[3]) is incremented by 5, becoming 93.
Finally, we read in four values of n and use them to increment a[i]:
- a[0] is incremented by 10, becoming 34.
- a[1] is incremented by 6, becoming 50.
- a[2] is incremented by 9, becoming 53.
- a[3] is incremented by 2, becoming 71.
So here are the answers:
- 1st line: 45:77:27:93
- 2nd line: 27:45:45:77
- 3rd line: 34:50:53:71
- 4th line: 34:50:53:71 -- (*dp) is equal to a.
Grading
3 points per line. I gave some partial credit to small arithmetic errors, and
some minor pointer confusion. On line 4, you got the full three points if lines 3
and 4 matched.
Here are answers of the various banks:
Input:
44 69 24 88
2 0 0 1
1 8 3 5
10 6 9 2
Output:
45:77:27:93:
27:45:45:77:
34:50:53:71:
34:50:53:71:
|
Input:
89 21 65 45
2 1 0 0
2 7 1 5
6 8 9 3
Output:
91:28:66:50:
66:28:91:91:
71:29:98:92:
71:29:98:92:
|
Input:
61 48 26 81
2 0 0 1
10 8 7 2
6 5 4 3
Output:
71:56:33:83:
33:71:71:56:
32:66:65:51:
32:66:65:51:
|
Input:
82 45 21 68
2 1 0 0
3 4 5 10
7 9 8 6
Output:
85:49:26:78:
26:49:85:85:
28:54:90:88:
28:54:90:88:
|
Input:
63 85 45 23
2 1 0 0
10 6 9 1
3 5 7 2
Output:
73:91:54:24:
54:91:73:73:
48:90:70:65:
48:90:70:65:
|
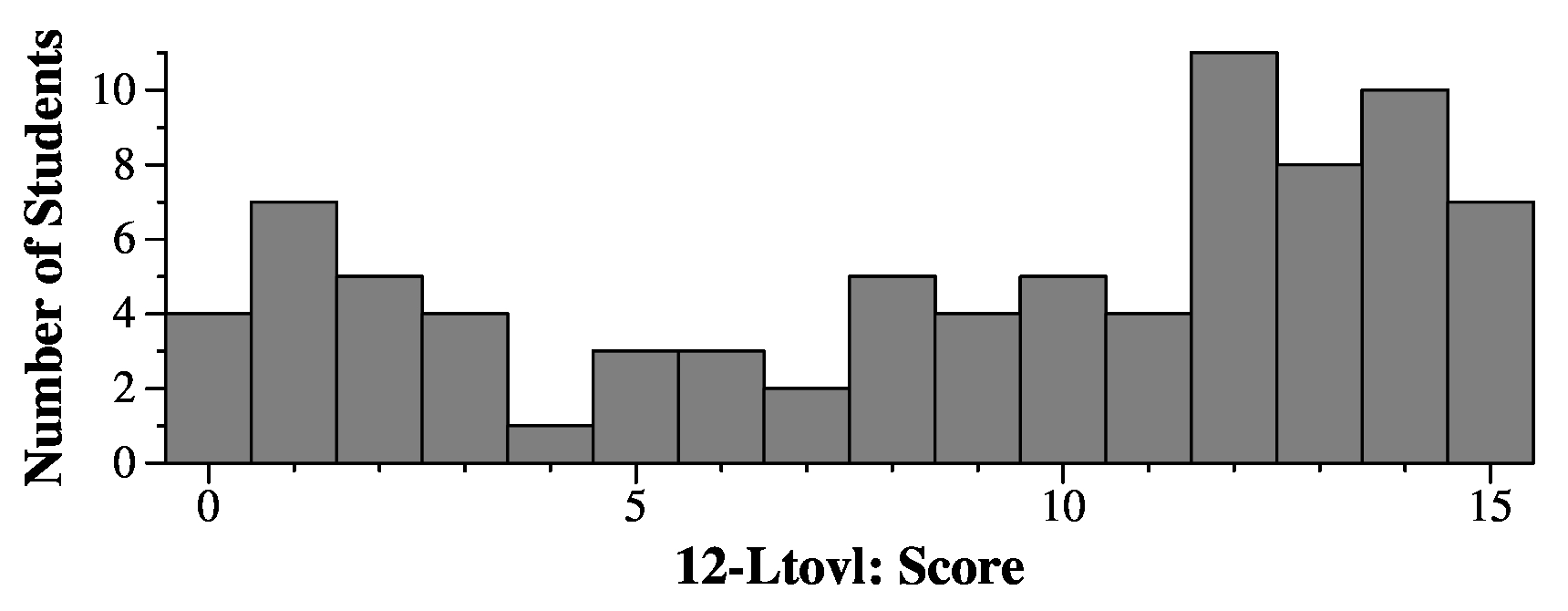
Question 12
This is a straightforward vector and list program:
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
vector < list <string> > ltovl(const list <string> &l)
{
list <string>::const_iterator lit;
vector < list <string> > rv;
rv.resize(2);
for (lit = l.begin(); lit != l.end(); lit++) {
if ((*lit)[0] >= 'A' && (*lit)[0] <= 'Z') {
rv[0].push_back(*lit);
} else {
rv[1].push_back(*lit);
}
}
return rv;
}
int main()
{
list <string> v;
vector < list <string> > rv;
list <string>::iterator lit;
string s;
int i;
while (cin >> s) v.push_back(s);
rv = ltovl(v);
for (i = 0; i < rv.size(); i++) {
cout << i;
for (lit = rv[i].begin(); lit != rv[i].end(); lit++) cout << " " << *lit;
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
Grading
Typically you started with 15 points and had deductions. If your code was too confused or
sparse, then you got some points along with "Please see the answer."
The most common deductions involved the proper use of iterators for the lists.
You can iterate through lists with integers. Also, the following tests whether c
is a capital letter:
if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z')
|
You do not need to memorize ASCII values.
You lost a half a point if you created two lists in ltovl(), and then you pushed
them onto a vector. That's making an unnecessary copy of each of the lists.