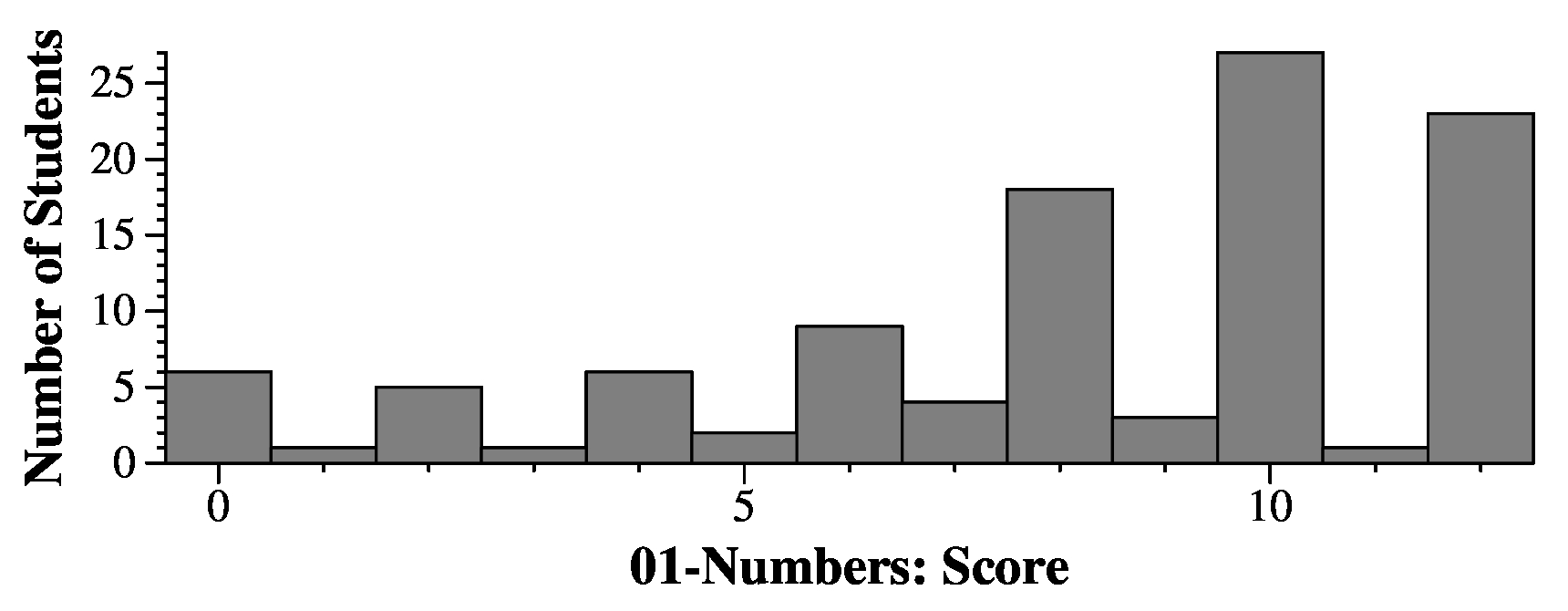
 |
For the rest of the question, your answer was recorded as "key-answer", where "key" was the number in Q1C.
Q1B: Here all of the questions were of the form 256x, where x is a digit between 1 and 9. This is 256*10 + x, so 0xa00 + x. Here are all of the answers:
2561 = 0xa01 2562 = 0xa02 2563 = 0xa03 2564 = 0xa04 2565 = 0xa05 2566 = 0xa06 2567 = 0xa07 2568 = 0xa08 2569 = 0xa09 |
Q1C: Here all of the questions were of the form 0xyz, where y was a digit between 1 and 5, and z was a digit between a and f. So, you had to multiply y by 16 and add z. Here are all of the answers:
0x1d-29 0x2c-44 0x2e-46 0x3c-60 0x3d-61 0x3e-62 0x4b-75 0x4d-77 0x5d-93 0x5e-94 |
Q1D: This was some permutation of 1011(b), 1001(9) and 1101(d):
0x1d-9db 0x2c-9db 0x2e-9bd 0x3c-9bd 0x3d-d9b 0x3e-d9b 0x4b-b9d 0x4d-db9 0x5d-d9b 0x5e-9bd |
Q1E: This is simply the number with two 0's after it:
0x1d-6d900 0x2c-6cd00 0x2e-28400 0x3c-d9c00 0x3d-7df00 0x3e-49a00 0x4b-74b00 0x4d-38200 0x5d-be100 0x5e-18900 |
Q1F: Now you just chop off the last digit:
0x1d-ca 0x2c-c4 0x2e-14 0x3c-ff 0x3d-57 0x3e-f4 0x4b-de 0x4d-c6 0x5d-3d 0x5e-12 |
 |
81 46 23 72 18 53 21 58 39 |
So, the vector is { "81", "46", "23", "72", "18", "53", "21", "58", "39", ?? }. The answers are:
Line 1: 91 --- the increment is to the first character, which is '8' to '9'. Line 2: 46 Line 3: 23 Line 4: 10 |
Here are all of the answers using the same keys as Question 1:
Q2A: 0x1d-82 0x2c-86 0x2e-Anything that ends with 8. 0x3c-93 0x3d-38 0x3e-28 0x4b-91 0x4d-72 0x5d-35 0x5e-65 Q2B 0x1d-36 0x2c-26 0x2e-76 0x3c-15 0x3d-38 0x3e-79 0x4b-46 0x4d-59 0x5d-59 0x5e-52 Q2C 0x1d-40 0x2c-18 0x2e-95 0x3c-57 0x3d-12 0x3e-88 0x4b-23 0x4d-72 0x5d-88 0x5e-76 Q2D - The answer is 10 for everyone.
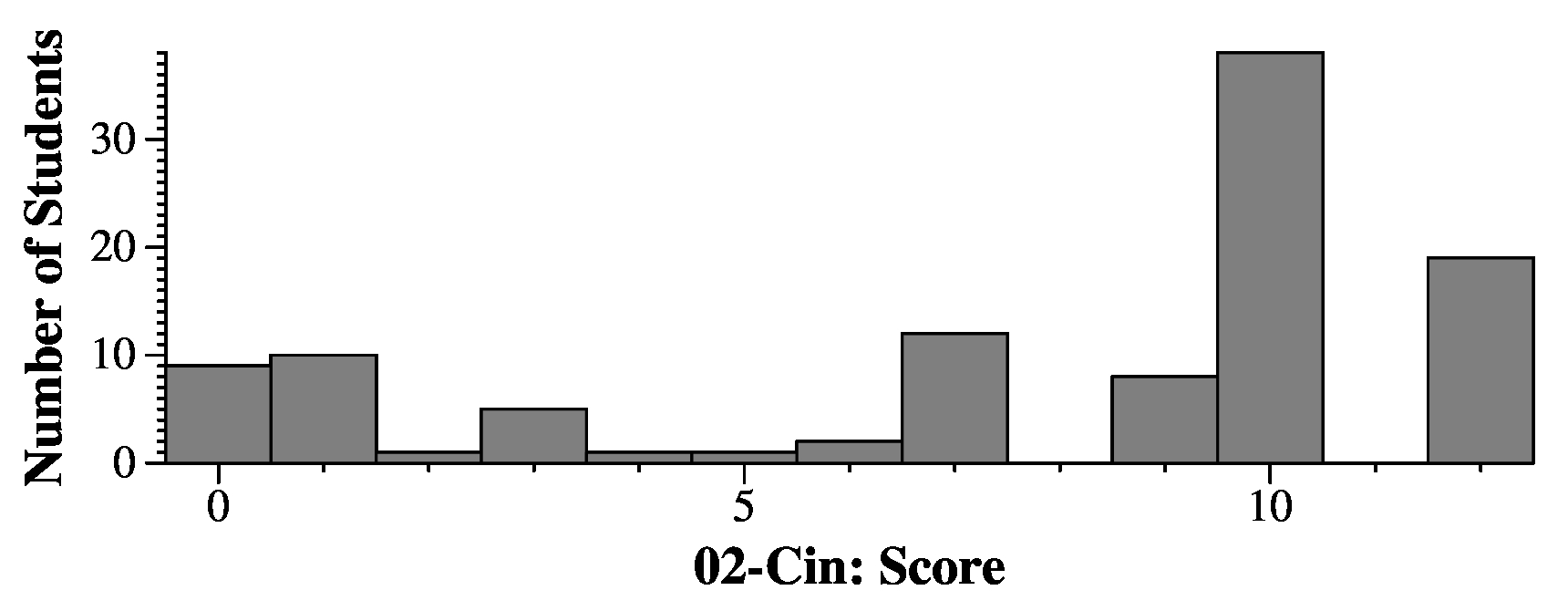 |
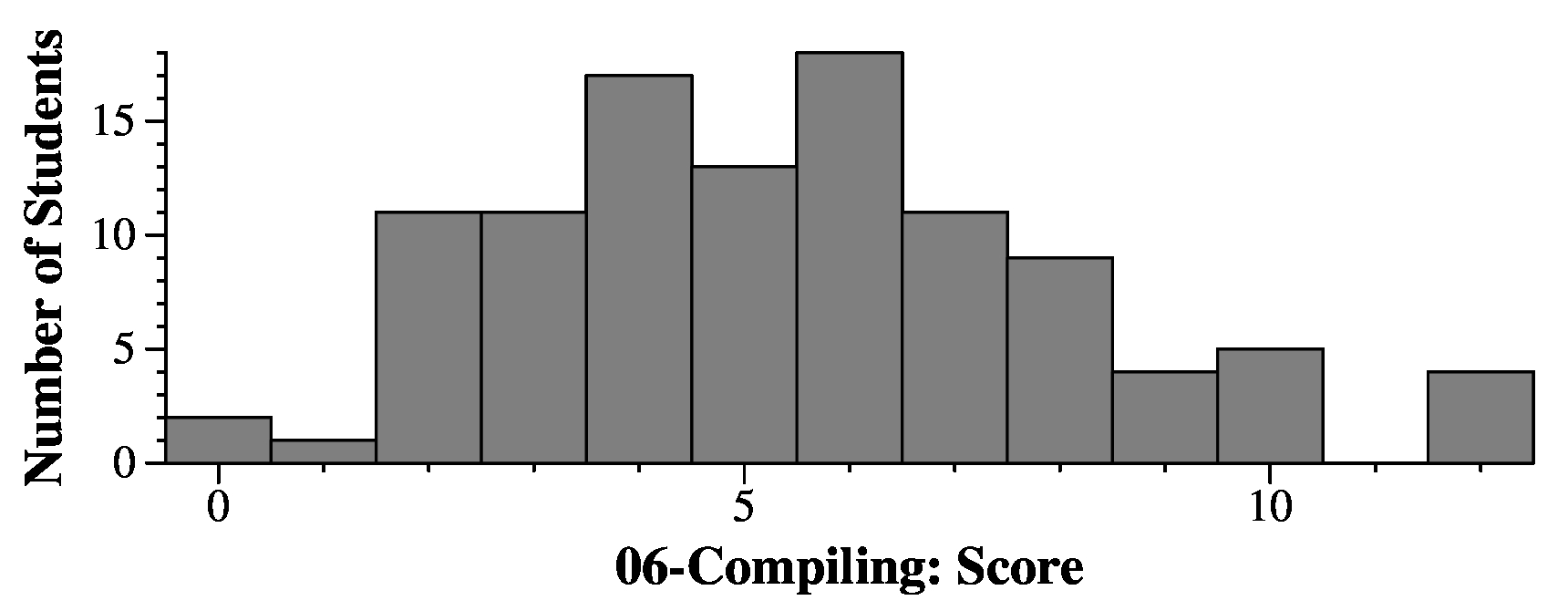
Q3B: The copy constructor is called when you pass an instance of a class as a non-reference parameter, and when you resize a vector using an instance of the class as a default. Those are the ones that I go over in class. You can also declare an instance of a class using another instance as a default:
E1 e1("Jim Plank");
E1 e2(e1); # This calls the copy constructor.
|
Q3C: If you use the default copy constructor, then it copies the value of cp from the old class. That's a pointer to the memory of the old class, and if the destructor of that is called, then the pointer is deleted. So instead, you need to define a copy constructor that allocates a new string for cp, copying it from the old string.
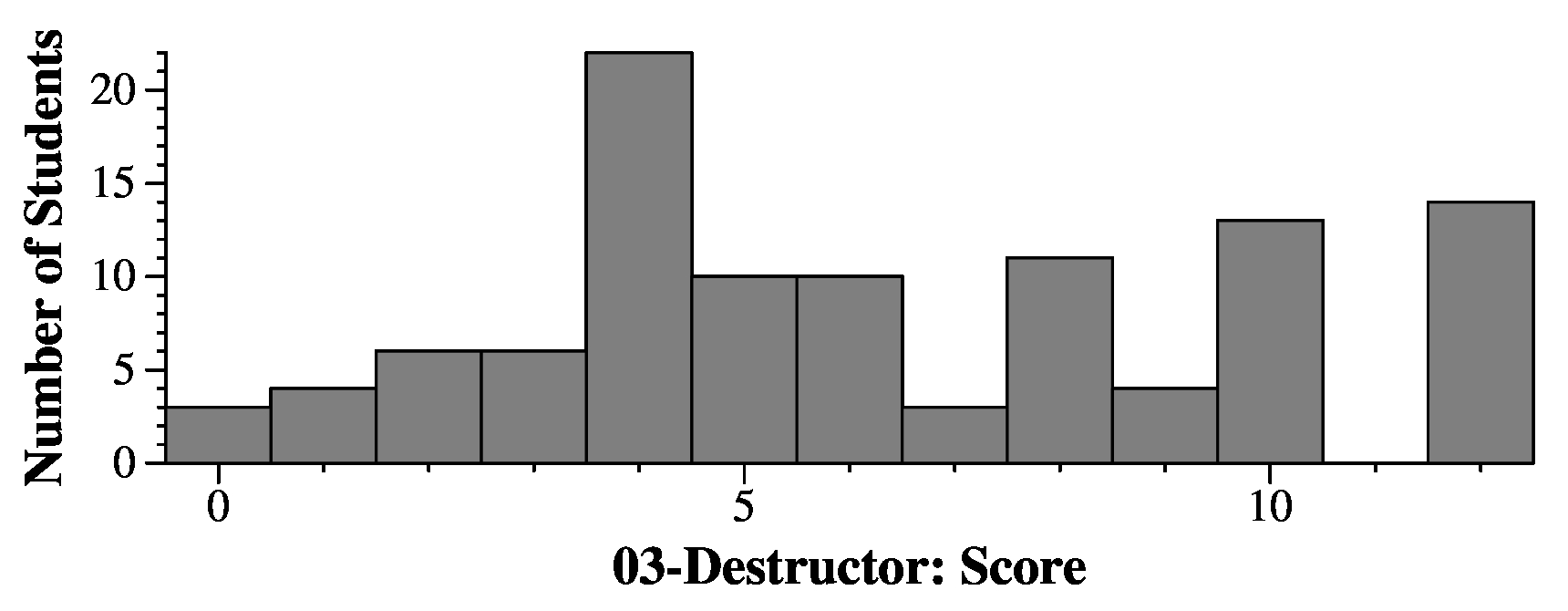 |
Q4C Aidan-Littleneck 1 Q4C Aubrey-Canoga 20 Q4C Dontonio-Rang 43 Q4C Julian-Norway 35 Q4C Madeline-Hallmark 23 Q4C Mia-Exigent 1 Q4C Nicholas-Commissary 4 Q4C Sarah-Hierarchy 10 Q4C Sophia-Pupil 9 Q4C Taylor-Downstairs 20 Q4D Aiden-Deferral 13 Q4D Carter-Strap 37 Q4D Chase-Carleton 12 Q4D Cooper 11 Q4D Gabriella-Cutback 26 Q4D Jack-Fibrosis 34 Q4D Lily-Jacksonian 5 Q4D Madeline-Pouch 1 Q4D Makayla-Domain 19 Q4D William-Percy 1 | Q4E Alyssa-Upton 19 Q4E Brooke-Pocketbook 7 Q4E Claire-Western 34 Q4E Isaac-Cent 37 Q4E Mackenzie-Intolerant 46 Q4E Michael-Chautauqua 37 Q4E Michael-Petticoat 23 Q4E Samantha-Espousal 22 Q4E Savannah-Kennecott 12 Q4E Xavier-Imperceivable 31 Q4F Alexander-Malaprop 4 Q4F Alexandra-William 8 Q4F Allison-Converge 6 Q4F Anthony-Mortician 46 Q4F Benjamin-Portico 8 Q4F Brayden-Laramie 34 Q4F Dontonio-Assure 43 Q4F Eva-College 42 Q4F Mason-Spline 43 Q4F Wyatt-Ester 8 | Q4G Bella-Impresario 21 Q4G Carson-Canvass 44 Q4G Christopher-Titillate 29 Q4G Gabriel-Close 40 Q4G John-Laurence 13 Q4G Logan-Xavier-Temptress 27 Q4G Madelyn-Tight 46 Q4G Sofia-Applicable 1 Q4G Thomas-Prince 14 Q4G Xavier-Scull 31 Q4H Chase-Film 2 Q4H Christopher-Phonon 5 Q4H Emma-Anarchy 36 Q4H Hannah-Scheme 2 Q4H Jonathan-Tibia 35 Q4H Logan-Badland 19 Q4H Michael-Angular 12 Q4H Natalie-Weird 12 Q4H Paige-Bet 6 Q4H Ryan-Ruminant 3 | Q4I Brianna-Demarcate 25 Q4I Brianna-Hastings-MD 21 Q4I Emma-Meld 1 Q4I Hunter-Blythe 26 Q4I Lucy-Hypertensive 6 Q4I Molly-Alveoli 20 Q4I Owen-Bantam-MD 16 Q4I Ryan-Newlywed 15 Q4I Tristan-Wack 4 Q4I Tyler-Inhumane-IV 1 Q4J Allison-Roar Q4J Brayden-Muddle Q4J Brooklyn-Fully Q4J Cooper-Summit Q4J Isaiah-Cutlass Q4J Jordan-Intervene Q4J Katelyn-Headphone Q4J Lily-Shreveport Q4J Maya-Rumpus Q4J Sydney-Sniffly |
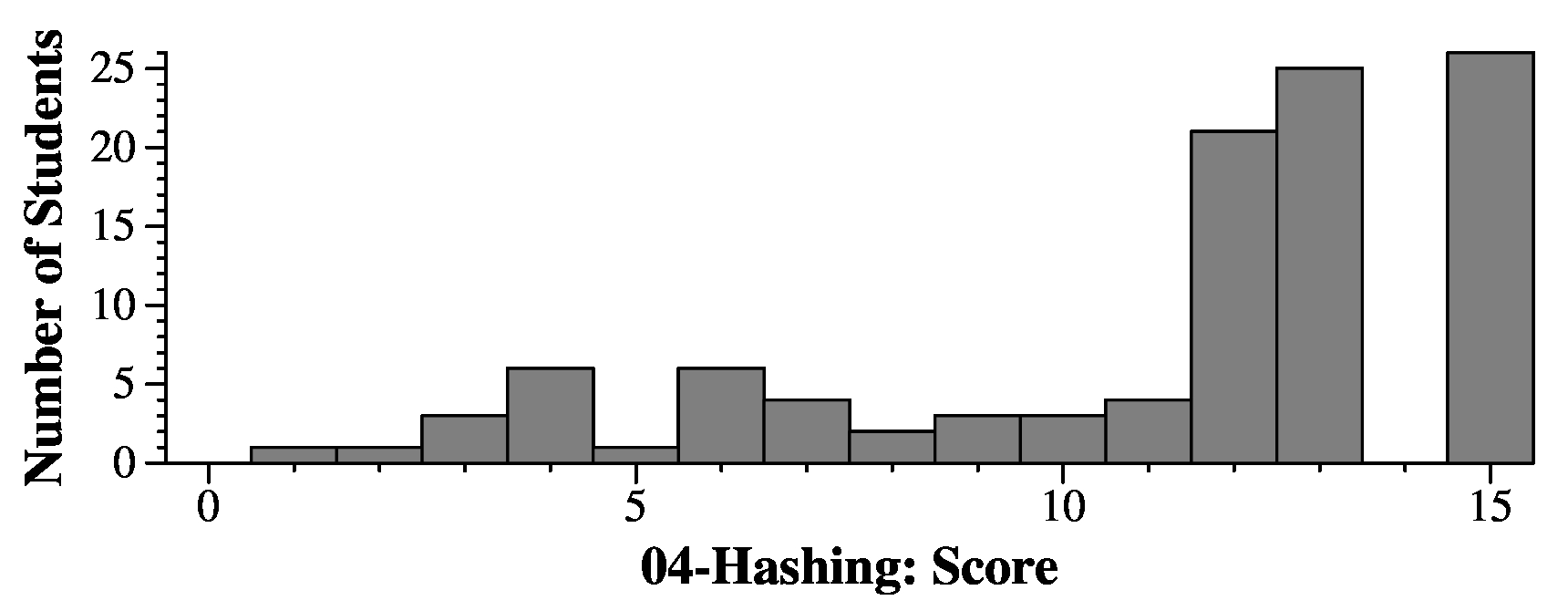 |
i=0:
vvec: { 20 }
wp[0] -------> 30 <------ a
^
l
| i=1:
vvec: { 20, 21 }
wp[0] -------> 30
wp[1] -------> 31 <------ a
^
l
| i=2:
vvec: { 20, 21, 22 }
wp[0] -------> 30
wp[1] -------> 31
wp[2] -------> 32 <------ a
^
l
| After the two lines before
the cout statements:
i=3:
vvec: { 20, 21, 22 }
wp[0] -------> 37 <------ a
wp[1] -------> 31
wp[2] -------> 32
^
l
|
As you can see, there are no memory leaks, because the three integers that we created with new are all accessible. The answer is the following:
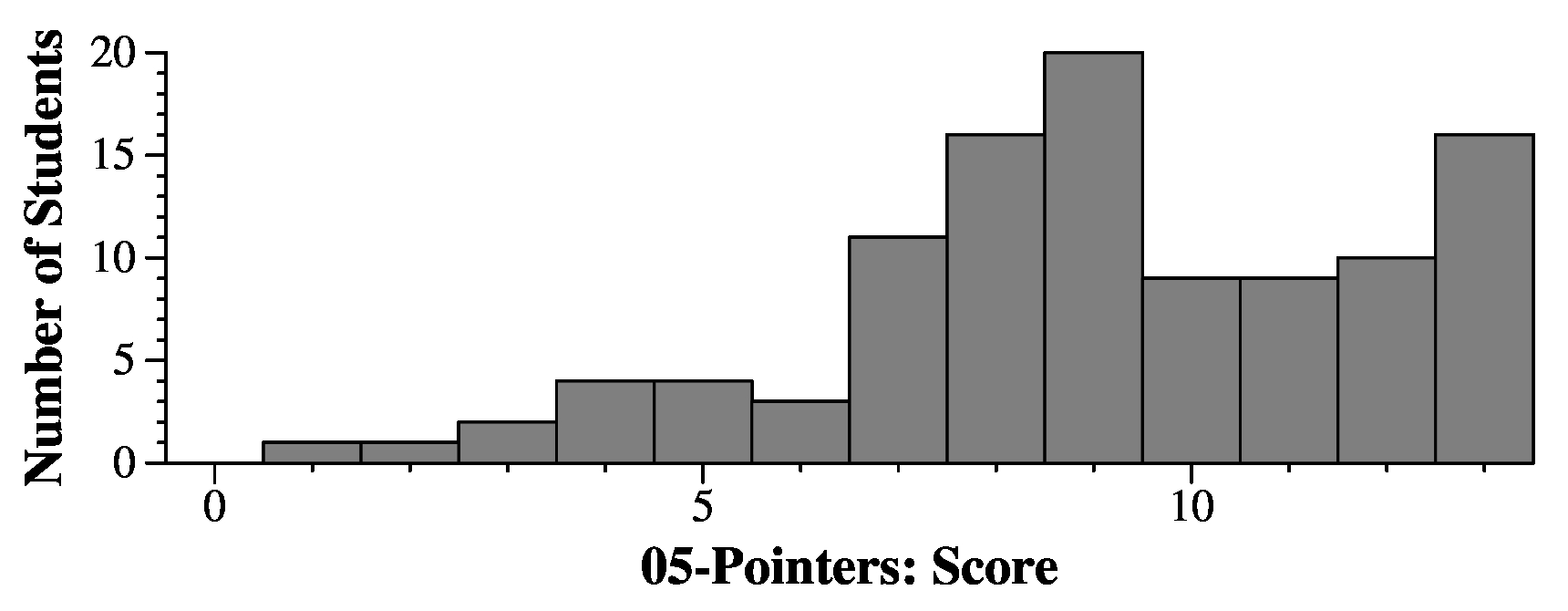
Q5A: 20 Q5B: 21 Q5C: 22 Q5D: 37 Q5E: 31 Q5F: 32 Q5G: 37 Q5H: 32 Q5I: N |
 |
Q6A:
The first thing that should jump out at you is the fact that the only constructor defined takes a parameter. I mentioned in class that I like to avoid this, because when you do this, you cannot simply declare variables of that type. Line 36 declares a variable of type C1, and since there's no non-parameterized constructor, that will be a compilation error.
The next problem is a public/protected problem. Since seed has been declared as protected, you cannot access it outside of the method implementations. For that reason, line 40 is a compiler error.
Q6B:
When you make s a const reference parameter, then the problems are going to come when you change it. So line 27 stands out as a problem. Lines 24 and 25 access s[0], but they don't change anything, so they are not problems. Line 26 also accesses s, but doesn't modify it, so it's not a problem. That leaves line 29 -- since E() does not declare that its string is const, we don't know whether E() modifies it or not -- that will be flagged as a compiler error.
Q6C:
We now make F() const, so it cannot modify seed. This is because seed is the only member variable in the class. So line 28 stands out as a problem. That's the only time seed can be modified, so where's the other problem? It's when you call D(). Since D() has not been declared as const, it could modify seed. So line 24 is the problem.
To summarize:
 |
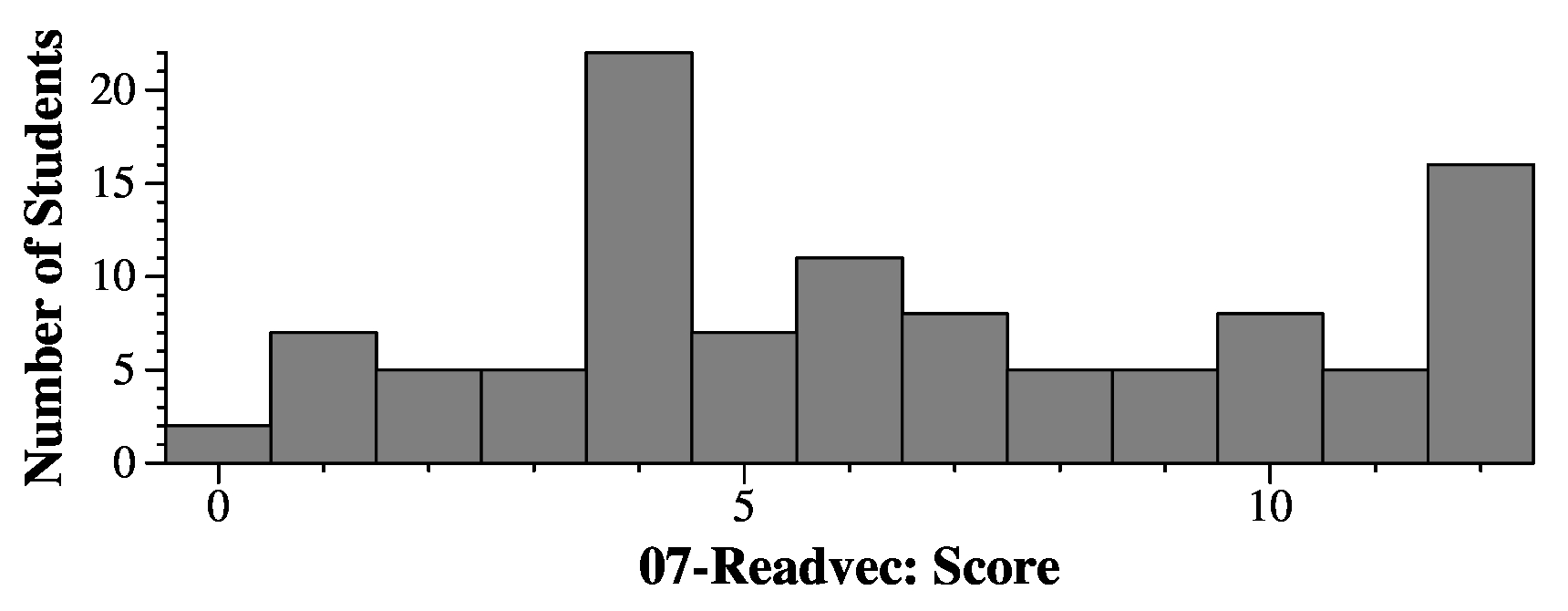
vector <string> ReadVec()
{
vector <string> rv;
istringstream ss;
string l, w;
if (!getline(cin, l)) throw (string) "Failed";
ss.str(l);
while (ss >> w) rv.push_back(w);
return rv;
}
|
ChatGPT gets this one right:
vector<string> ReadVec() {
string line;
if (!getline(cin, line)) {
throw string("Failed");
}
vector<string> result;
istringstream iss(line);
string word;
while (iss >> word) {
result.push_back(word);
}
return result;
}
|
 |
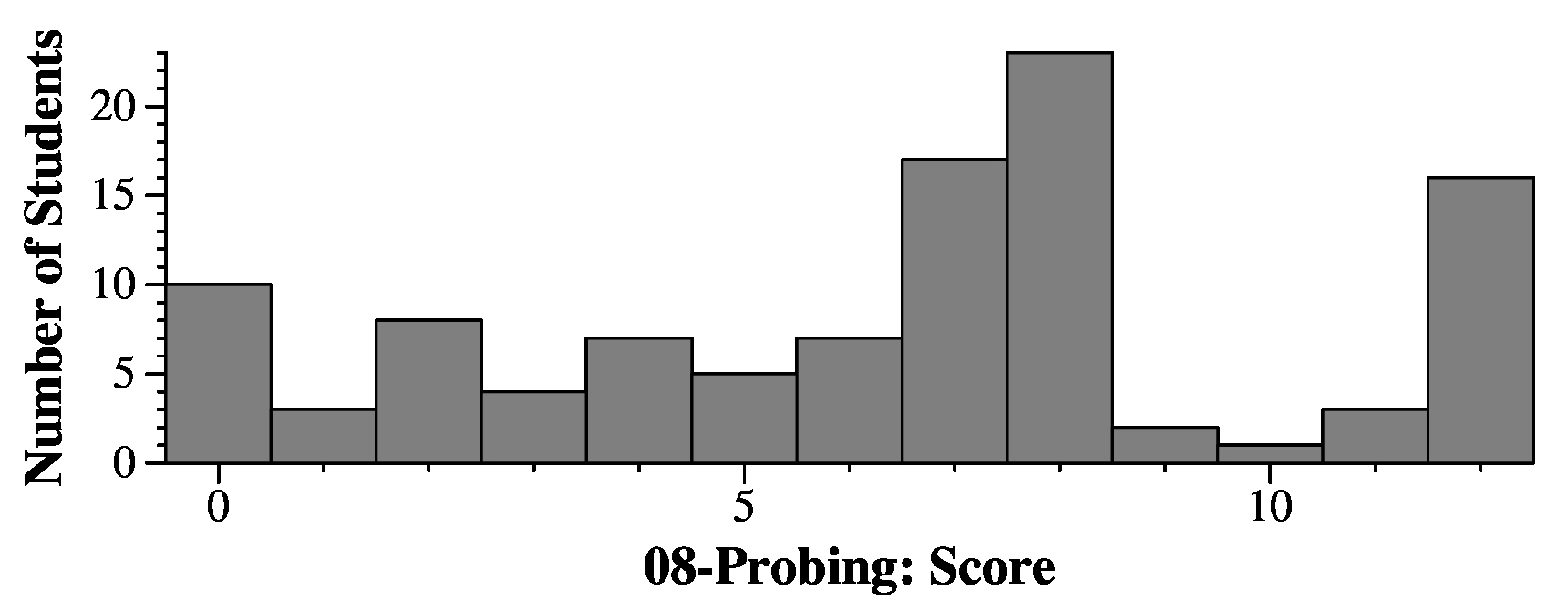
bool find(const string &s, const vector <string> &ht)
{
int h, i, index;
h = hash(s);
for (i = 0; i < (int) ht.size(); i++) {
index = (h + i * i) % ht.size();
if (ht[i] == "") return false;
if (ht[i] == s) return true;
}
return false; // Full hash table without s.
}
|
Here's Chat GPT's answer (which is correct, even if it doesn't follow my programming style):
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int hash(const string &s); // Provided elsewhere
bool find(const string &s, const vector<string> &ht) {
int size = ht.size();
int h = hash(s) % size;
// Quadratic probing
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int pos = (h + i * i) % size;
if (ht[pos] == "") {
// Empty slot — s not in the table
return false;
}
if (ht[pos] == s) {
// Found the string
return true;
}
// Otherwise, continue probing
}
// Should never reach here (table not full)
return false;
}
|
With grading, you typically started with 12 points, and then were deducted. The most common deduction was when you traversed the entire table and didn't exit early when you saw an empty string. That was -4, and I was shocked at how many answers had this problem. Basically, it's omiting the test for "" above. There were similar problems where you exit when you see "", but don't exit when you find the string.
 |